Stainless steel is an important material of choice in various industries. Among the many grades available, 304 and 316 stainless steel stand out. The two grades have different compositions and properties, which affects their usefulness in different applications.

About Stainless Steel Grades
Stainless steel is categorized into various grades based on its chemical composition and properties. The primary elements that define these grades are chromium, nickel, and, in some cases, molybdenum.
- 304 Stainless Steel: This grade typically contains about 18% chromium and 8% nickel, which gives it good corrosion resistance and formability. It is often referred to as "18/8" stainless steel due to this composition.
- 316 Stainless Steel: This grade includes approximately 16% chromium, 10% nickel, and 2% molybdenum. The addition of molybdenum enhances its resistance to corrosion, particularly in chloride-rich environments.
Both grades belong to the austenitic stainless steel family, which is characterized by a face-centered cubic crystal structure. This structure provides excellent strength and ductility, making both grades suitable for a variety of applications. .
Differences Between 304 and 316 Stainless Steel
The differences between 304 and 316 stainless steel are primarily based on their chemical compositions, which significantly influence their performance in various environments. Here are the key distinctions:
Feature | 304 Stainless Steel | 316 Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|
Chemical Composition | 18% chromium, 8% nickel | 16% chromium, 10% nickel, 2-3% molybdenum |
Corrosion Resistance | Moderate resistance to corrosion | High resistance, especially to chlorides |
Molybdenum Content | None | Present (2-3%) |
Cost | Generally lower cost | Typically higher cost (about 40% more) |
Temperature Resistance | Good for moderate temperatures | Better performance at high temperatures |
Applications | General use in food and beverage | Marine, chemical processing, and medical applications |
The addition of molybdenum in 316 stainless steel enhances its ability to resist pitting and crevice corrosion, particularly in chloride environments such as coastal areas or industrial settings. This makes 316 a preferred choice for applications exposed to harsh conditions.
Thus, while both grades share many properties and are suitable for various applications, the choice between 304 vs 316 stainless steel often depends on the specific environmental challenges and budget considerations.

Benefits of Using 304 Stainless Steel
304 stainless steel is one of the most widely used grades of stainless steel, and it offers several key benefits that make it suitable for a variety of applications. Here are the primary advantages:
- Corrosion Resistance: 304 stainless steel can withstand exposure to a range of chemicals and is particularly effective at resisting oxidation, making it suitable for applications in food processing and kitchen work.
- Durability: It can withstand significant stresses and pressures, making it a reliable choice for structural applications.
- EASY TO MANUFACTURE: 304 stainless steel is easy to machine. It can be cut, welded and shaped without losing its structural integrity. This flexibility is widely used in manufacturing processes.
- HIGH TEMPERATURE RESISTANT: Maintains its properties even at high temperatures, with a melting point range of 2,550°F to 2,650°F.
- LOW MAINTENANCE: Due to its corrosion resistance and durability, 304 stainless steel requires very little maintenance.
The combination of these advantages makes 304 stainless steel a versatile material suitable for a wide range of applications, including kitchen equipment, storage tanks, piping systems and building elements. Its characteristics can meet the needs of various industries and it also has high durability.
Benefits of Using 316 Stainless Steel
316 stainless steel is known for its superior properties, making it a preferred choice in demanding environments. Here are the primary benefits of using 316 stainless steel:
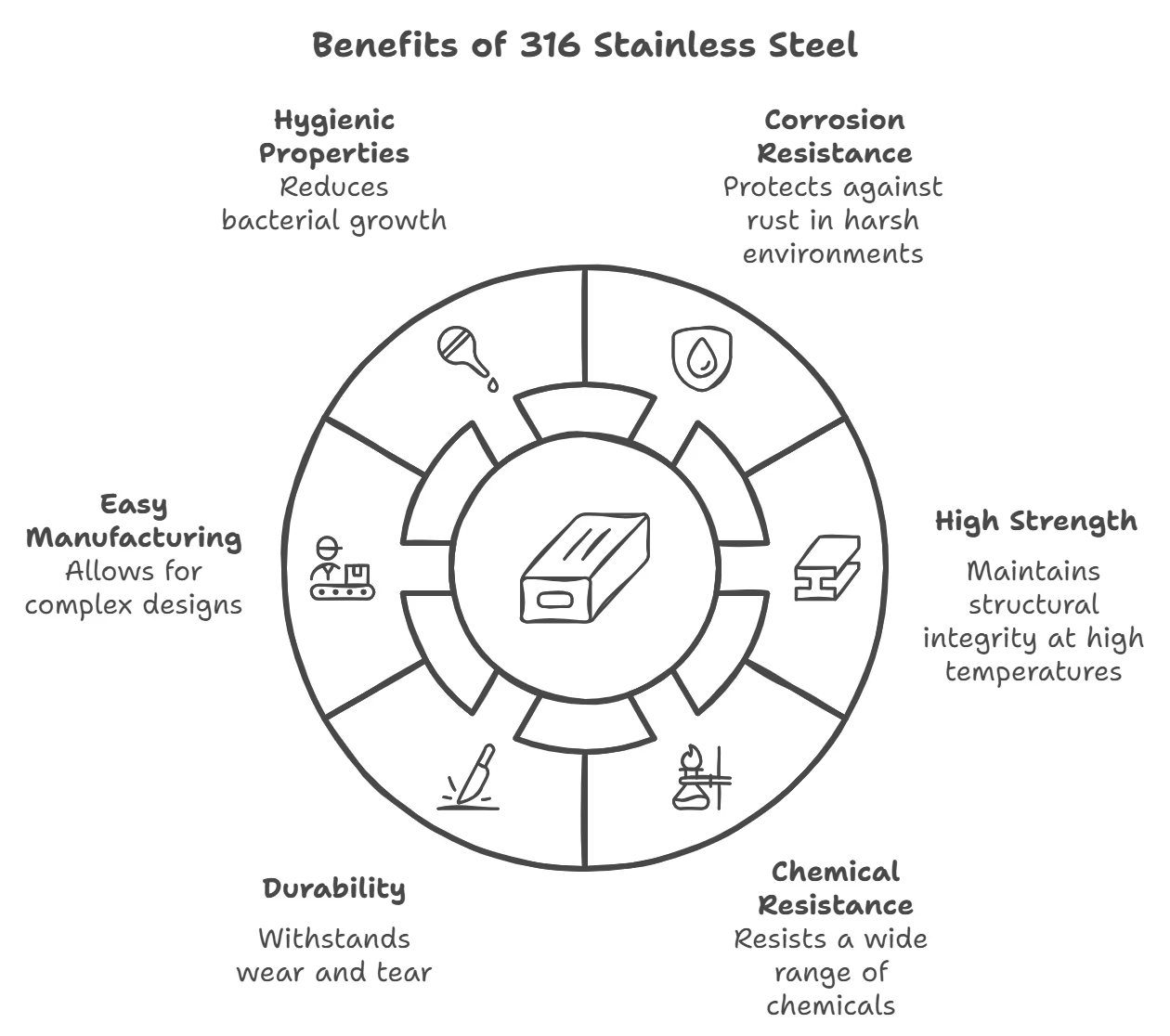
- Enhanced Corrosion Resistance: 316 stainless steel has high corrosion resistance, especially in chloride environments. This makes it suitable for use in saltwater environments such as the ocean.
- Molybdenum Added: The presence of molybdenum increases its resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion.
- HIGH STRENGTH AT HIGH TEMPERATURE: 316 maintains its strength and structural integrity at higher temperatures better than 304.
- Chemical Resistance: It is resistant to a wide range of chemicals and is suitable for use in the chemical processing industry, pharmaceutical and food production industries.
- Durability: 316 stainless steel is extremely durable and can withstand harsh conditions without significant wear or degradation.
- EASY TO MANUFACTURE: Similar to 304, 316 stainless steel can be easily welded and formed. Its workability allows for complex designs and structures during manufacturing.
- Hygienic Properties: The smooth surface finish of 316 stainless steel reduces bacterial growth, making it an excellent choice for food and medical industry applications.
316 stainless steel is suitable for corrosive and high temperature environments. Its characteristics enable it to maintain a low failure rate in high-intensity working environments.
Is It Worth the Extra Cost?
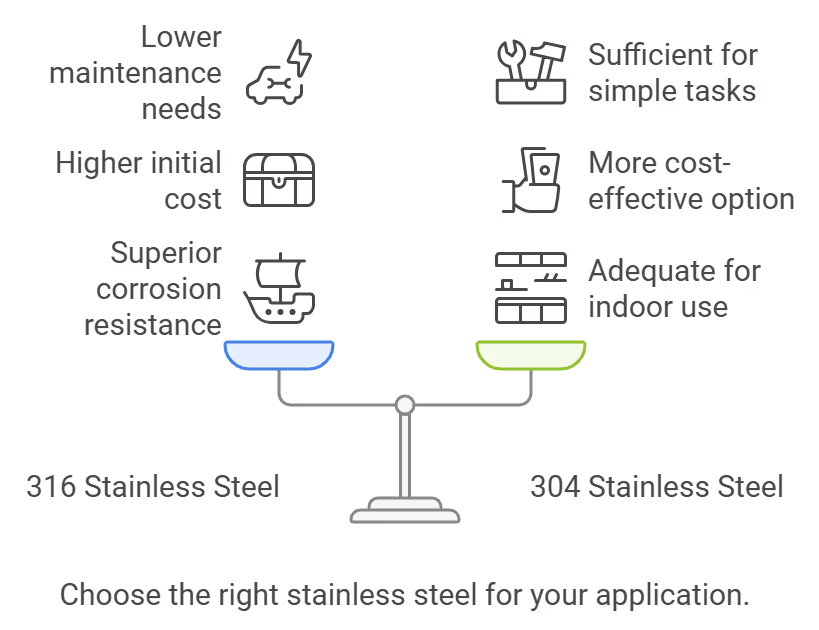
Corrosion Resistance
316 stainless steel offers significantly better corrosion resistance than 304 stainless steel due to its higher nickel content and the addition of molybdenum. This makes 316 particularly effective in environments exposed to chlorides, such as marine applications, chemical processing, and food service. For example, 316 stainless steel is often used in coastal areas where salt exposure can rapidly degrade 304 stainless steel. In contrast, 304 stainless steel is suitable for less corrosive environments but will fail in applications involving strong acids or chlorides.
Durability
Both grades exhibit high durability; however, 316 stainless steel is generally more resilient under harsh conditions. Its resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion extends the lifespan of components made from this material. For instance, in chemical processing facilities where equipment faces continuous exposure to aggressive substances, 316 stainless steel can last significantly longer than 304, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
Application Suitability
The choice between 304 and 316 stainless steel should be guided by the specific application:
- 304 Stainless Steel: Commonly used in applications such as kitchen equipment, appliances, and indoor structures where exposure to corrosive elements is minimal.
- 316 Stainless Steel: Preferred for applications that require enhanced corrosion resistance, such as marine environments, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and food processing equipment.
So, if the application involves exposure to harsh chemicals or saline environments, 316 stainless steel is often the better choice.
Long-Term Savings
While 316 stainless steel typically costs around 40 percent more than 304 stainless steel initially, it can result in significant long-term savings. The durability and corrosion resistance of 316 lead to lower maintenance costs and a longer service life.
For example, in a marine environment, equipment made from 304 may require replacement within a few years due to corrosion, while 316 can last a decade or more without significant degradation. This longevity reduces replacement costs and minimizes downtime associated with repairs.
In industries like food processing or pharmaceuticals, using 316 stainless steel can prevent contamination risks associated with corrosion. The financial impact of equipment failure—due to lost production time or product recalls—can be substantial. Therefore, investing in 316 stainless steel often results in lower total cost of ownership over time when considering both initial investment and ongoing operational costs.
FAQs about 304 vs 316 Stainless Steel
What are the main differences between 304 and 316 stainless steel?
The primary differences between 304 and 316 stainless steel lie in their chemical compositions and corrosion resistance. 304 stainless steel contains approximately 18% chromium and 8% nickel, while 316 stainless steel includes 16% chromium, 10% nickel, and 2-3% molybdenum. The addition of molybdenum in 316 enhances its resistance to corrosion, especially in chloride environments, making it more suitable for marine or chemical applications.
When should I choose 304 stainless steel over 316 stainless steel?
You should consider choosing 304 stainless steel when your application involves mild environments, such as food processing, kitchen equipment, or indoor architectural elements. It is cost-effective and provides adequate corrosion resistance for these uses. However, if your application involves exposure to harsh chemicals or saltwater, then opting for 316 stainless steel would be advisable.
What are the benefits of using 316 stainless steel?
The benefits of using 316 stainless steel include superior corrosion resistance, particularly against chlorides, making it ideal for marine and chemical processing applications. It also maintains high strength at elevated temperatures and has excellent durability in harsh environments. Additionally, its hygienic properties make it suitable for medical and food processing applications.
Can I use 304 stainless steel in outdoor applications?
While you can use 304 stainless steel in outdoor applications, it is not as resistant to corrosion as 316 stainless steel. If the environment is prone to moisture or salt exposure, such as coastal areas, it is better to choose 316 stainless steel to avoid rusting and degradation over time. For less demanding outdoor uses where aesthetics and cost are priorities, 304 may still be a viable option.
What are some common applications for both 304 and 316 stainless steel?
Common applications for 304 stainless steel include kitchen equipment, food processing machinery, storage tanks, and architectural features. In contrast, 316 stainless steel is often used in marine environments, chemical processing equipment, medical devices, and any application requiring high corrosion resistance. Understanding these applications helps in selecting the appropriate grade based on specific needs.


