Aluminum alloys are widely used in various industries due to their excellent properties. Among these alloys, aluminum 6065 and 6005 are common choices. This article will explore the differences between aluminum 6065 and 6005, focusing on their composition, mechanical properties, applications, extrusion characteristics and cost considerations.

What are Aluminum Alloys?
Aluminum alloys are materials created by combining aluminum with other elements to improve specific properties. These alloys enhance characteristics like strength, corrosion resistance, and machinability compared to pure aluminum. The alloying process involves melting aluminum and adding elements such as copper, magnesium, silicon, and zinc.
Aluminum alloys are classified into 2 main categories:
- Wrought Alloys: These are shaped through mechanical processes like rolling or extrusion. They are often used in applications requiring high strength and ductility.
- Casting Alloys: These are formed by pouring molten aluminum into molds. They are ideal for creating complex shapes and components.
Each aluminum alloy is identified by a four-digit code, which indicates its composition and specific properties. For instance, the 6000 series includes alloys primarily made with magnesium and silicon, which are known for their good corrosion resistance and workability.
Composition Comparison: Aluminum 6065 vs 6005
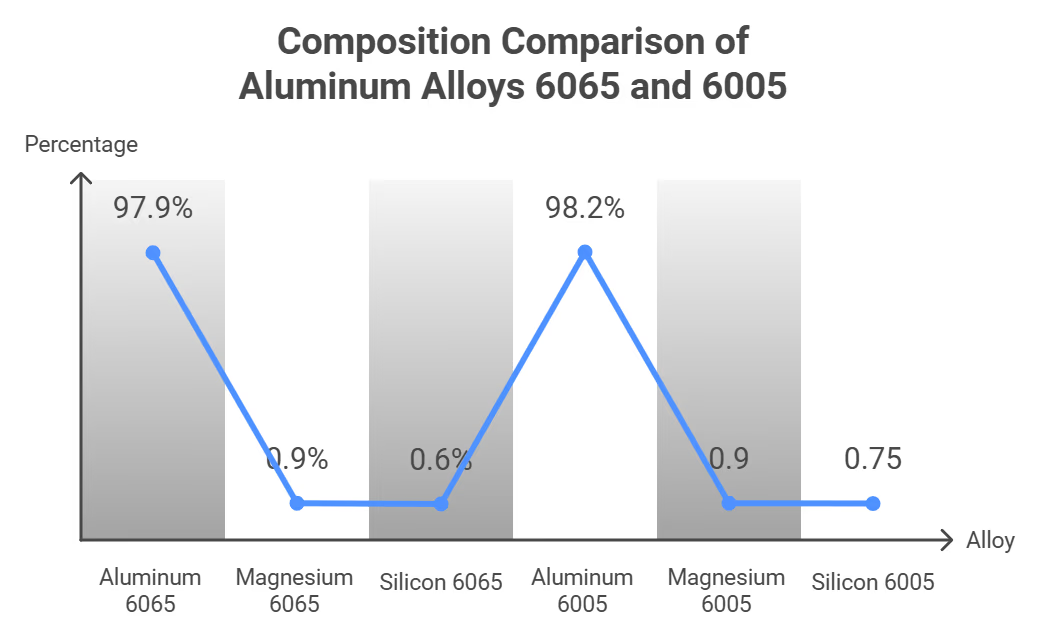
Compare Aluminum 6065 vs 6005. Both alloys belong to the 6000 series and contain primarily magnesium and silicon as alloying elements. However, they differ in their specific ingredient percentages, which can affect their performance and application.
Chemical Composition
- Aluminum 6065 typically contains:
- Aluminum: Approximately 97.9%
- Magnesium: 0.6% - 1.2%
- Silicon: 0.4% - 0.8%
- Aluminum 6005 generally has:
- Aluminum: Approximately 98.2%
- Magnesium: 0.6% - 1.2%
- Silicon: 0.6% - 0.9%
The slight variations in silicon content can influence the mechanical properties of each alloy. For example, aluminum 6065 has a slightly lower silicon percentage compared to aluminum 6005, which may affect its strength and corrosion resistance.
Workability and Processing
Both aluminum alloys offer good workability but differ slightly in their processing capabilities:
- Aluminum 6065 is known for its excellent casting performance and plasticity, allowing it to be shaped into various forms easily.
- Aluminum 6005 also provides good processing performance, particularly in welding and forming operations. It can be welded using various methods such as argon arc welding and resistance welding.
Summary of Composition Comparison
While both aluminum alloys share similarities as members of the same series, their specific compositions lead to distinct characteristics:
- Aluminum 6065 is often chosen for applications requiring good strength and formability.
- Aluminum 6005 is preferred for its higher strength and excellent weldability.
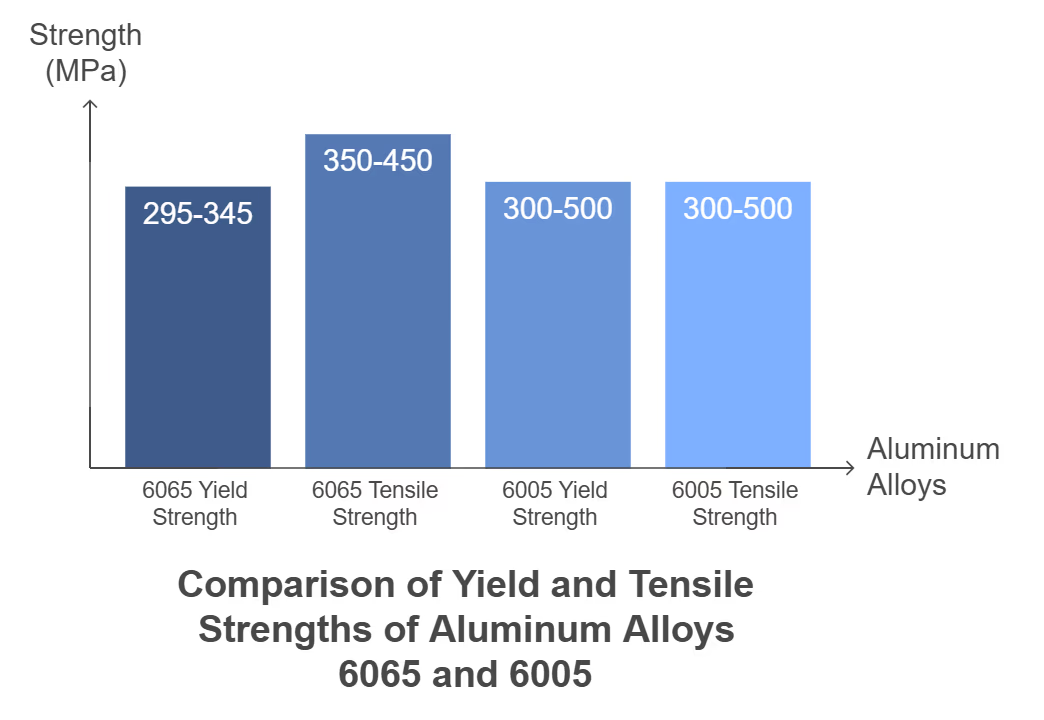
Mechanical Properties
Mechanical properties are a key aspect to consider when comparing aluminum 6065 vs 6005. These properties determine how each alloy behaves under stress, temperature changes and other environmental factors. The two alloys exhibit different mechanical properties.
Aluminum 6065 Mechanical Properties
Aluminum 6065, particularly in the T6 temper, showcases the following mechanical properties:
- Yield Strength: Approximately 270 MPa to 310 MPa
- Tensile Strength: Typically ranges from 310 MPa to 450 MPa
- Elongation at Break: About 11%
- Brinell Hardness: Approximately 95
- Elastic Modulus (Young's Modulus): 68 GPa (9.9 x 10^6 psi)
These properties indicate that aluminum 6065 has a good balance of strength and ductility, making it suitable for applications requiring both toughness and formability. The elongation percentage reflects its ability to deform without breaking, which is beneficial in structural applications.
Aluminum 6005 Mechanical Properties
Aluminum 6005 also presents robust mechanical properties, especially in the T6 temper:
- Yield Strength: Generally around 250 MPa to 300 MPa
- Tensile Strength: Ranges from approximately 300 MPa to 400 MPa
- Elongation at Break: About 11%
- Brinell Hardness: Approximately 95
- Elastic Modulus (Young's Modulus): 69 GPa (10 x 10^6 psi)
Similar to aluminum 6065, aluminum 6005 exhibits a good combination of strength and ductility. The tensile strength is slightly lower than that of aluminum 6065, but it remains suitable for many structural applications.
Comparison of Mechanical Properties
Property | Aluminum 6065 | Aluminum 6005 |
|---|---|---|
Yield Strength | 270 - 310 MPa | 250 - 300 MPa |
Tensile Strength | 310 - 450 MPa | 300 - 400 MPa |
Elongation at Break | ~11% | ~11% |
Brinell Hardness | ~95 | ~95 |
Elastic Modulus | 68 GPa | 69 GPa |
Both aluminum alloys exhibit strong mechanical properties suitable for various applications.
- Aluminum 6065 tends to have a higher yield and tensile strength, making it preferable for demanding structural components.
- Aluminum 6005, while slightly lower in strength, still offers excellent performance and is widely used in applications where good corrosion resistance and weldability are essential.
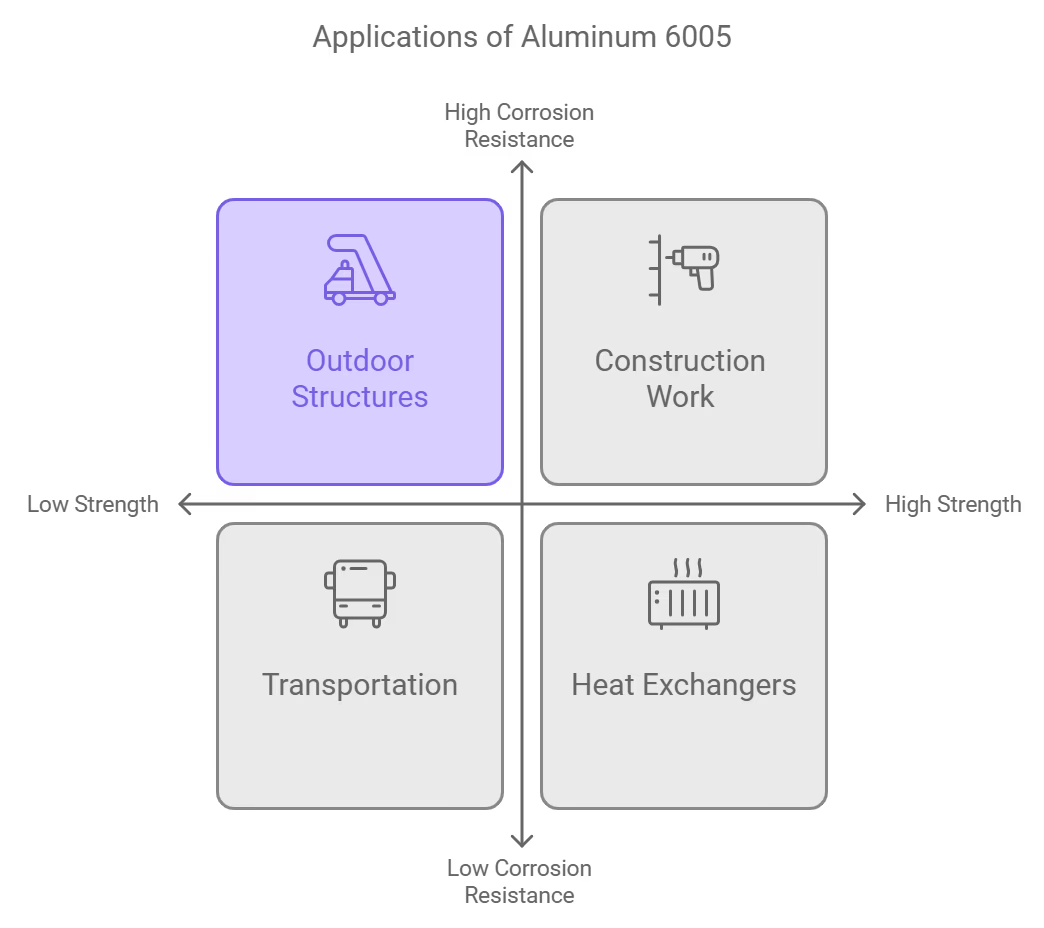
Applications of Aluminum 6065 vs 6005
Aluminum 6065 and 6005 are used in various industries due to their good properties. Understanding the specific applications of each alloy can help you choose the right one for your project.
Applications of Aluminum 6065
Aluminum 6065 is known for its strength and excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for a variety of applications, including:
- Marine Applications: 6065 aluminum is resistant to seawater corrosion and is suitable for use in marine environments. Typical applications include ship hulls, gangways and dock structures.
- Building components: Aluminum 6065 is commonly used in the construction of window frames, doors and curtain walls.
- Structural Components: This alloy is used in structural applications requiring precise mechanical properties. For example, support beams and frames require high strength and resistance to environmental factors.
- Extruded Parts: Aluminum 6065 is suitable for producing complex extruded shapes for structural and mechanical parts.
Applications of Aluminum 6005
Aluminum 6005 is recognized for its medium strength and excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for a different range of applications:
- Construction and Structural Work: Aluminum 6005 is often used in construction applications such as structural beams, railings, scaffolding, and other load-bearing components. Its higher strength compared to some other alloys makes it ideal for these purposes.
- Transportation: This alloy is commonly used in the automotive industry for manufacturing parts like frames, connectors, and chassis components. Its lightweight nature contributes to improved fuel efficiency.
- Heat Exchangers: Aluminum 6005 is suitable for use in heat exchangers and thermal control systems due to its thermal conductivity and resistance to high temperatures.
- Outdoor Applications: Given its good corrosion resistance, aluminum 6005 is frequently used in outdoor structures such as platforms, ladders, and handrails that must withstand exposure to the elements.
Application Type | Aluminum 6065 | Aluminum 6005 |
|---|---|---|
Marine | Boat hulls, gangways | Limited use |
Architectural | Window frames, doors | Architectural trim |
Structural Components | Support beams | Load-bearing structures |
Extruded Parts | Custom profiles | Various extruded shapes |
Transportation | Limited use | Automotive parts |
Heat Exchangers | Rarely used | Commonly used |
Extrusion Characteristics
Extrusion is a manufacturing process for aluminum alloys that can create complex shapes and profiles. Aluminum 6065 and 6005 are popular choices for extrusion due to their favorable properties, but they exhibit unique properties that affect their performance in the process.
Aluminum 6065 Extrusion Characteristics
- Extrudability: Aluminum 6065 is known for its excellent extrudability, which allows it to be formed into complex shapes with high precision. Its lower silicon content compared to other alloys helps achieve smooth surfaces and detailed contours.
- Tempering Options: The most common temper state for aluminum 6065 is T6, which involves solution heat treatment followed by artificial aging. This tempering increases the strength and ductility of the alloy, making it suitable for applications requiring complex geometries.
- Surface Finish: The surface finish of extruded aluminum 6065 is generally good and suitable for applications where aesthetics are important. It responds well to the anodizing process, further improving its corrosion resistance and aesthetics.
Aluminum 6005 Extrusion Characteristics
- Strength and Durability: Compared to 6065, Aluminum 6005 is stronger and is ideal for those structural applications that require high load-bearing capacity. Its higher silicon content lowers the melting point and also enhances its extrudability.
- Tempering Options: Like 6065, aluminum 6005 is typically produced with a T6 temper. This treatment improves its mechanical properties, allowing it to withstand higher stresses in structural applications.
- Bending Properties: Aluminum 6005 has excellent bending properties, making it suitable for applications requiring curved or shaped profiles. However, its increased strength makes it more difficult to machine than softer alloys.
Comparison of Extrusion Characteristics
Characteristic | Aluminum 6065 | Aluminum 6005 |
|---|---|---|
Extrudability | Excellent; intricate shapes | Good; suitable for structural shapes |
Common Temper | T6 | T6 |
Surface Finish | Good; suitable for anodizing | Good; better mill surface finish |
Strength | Moderate | Higher strength |
Bending Properties | Good; easier to shape | Excellent; strong but harder to shape |
Both aluminum 6065 and 6005 are effective materials for extrusion but serve different purposes based on their characteristics:
- Aluminum 6065 is favored for applications requiring intricate designs and good surface finishes due to its excellent extrudability and aesthetic qualities.
- Aluminum 6005, with its higher strength and durability, is more suited for structural applications where load-bearing capacity is essential.
Cost Considerations
When evaluating aluminum 6065 vs. 6005, cost is an important factor in material selection. Both alloys are part of the 6000 series and their prices may vary depending on a variety of factors.
General Cost Comparison
- Aluminum 6065: This alloy is generally more expensive than Aluminum 6005. The higher cost due to its composition and properties allows for tighter tolerances and better performance in some applications. The manufacturing process of aluminum 6065 may also involve additional steps to achieve its desired properties, adding to the overall cost.
- Aluminum 6005: Generally, aluminum 6005 is cheaper than 6065. Its cost-effectiveness makes it a popular choice for structural applications that require high strength but do not require the exacting specifications of 6065. Easier processing requirements and wider availability also contribute to its lower price.
Factors affecting cost
There are several factors that affect the cost of aluminum alloys, including:
- Raw Material Prices: The cost of aluminum fluctuates based on market demand and supply chain dynamics. Price changes in alloying elements such as magnesium and silicon also affect the final price of the alloy.
- Manufacturing Process: The complexity of the manufacturing process affects cost. Aluminum 6065 may require more precise machining or additional handling compared to aluminum 6005, resulting in higher production costs.
- Market Demand: Demand for specific alloys across various industries may drive prices up or down. If a certain alloy is better suited for certain applications, its demand may increase, affecting its market price.
- BUY IN BULK: Buying in bulk usually comes with discounts. Companies that purchase large quantities of any one alloy may be able to negotiate better prices, affecting overall costs.
While both aluminum 6065 and 6005 are valuable materials with distinct properties, their costs can differ significantly:
- Aluminum 6065 tends to be more expensive due to its enhanced properties and tighter tolerances.
- Aluminum 6005 is generally more cost-effective, making it suitable for a wide range of structural applications where high strength is required without the need for precise specifications.
FAQs about Aluminum 6065 vs 6005
What are the minimum wall thickness limitations for 6065 vs 6005 in extrusion?
6065 can achieve thinner wall sections down to 1.2mm, while 6005 typically requires a minimum of 1.5mm wall thickness due to its higher silicon content and strength characteristics.
How do temperature fluctuations affect the dimensional stability of 6065 vs 6005?
6065 exhibits better dimensional stability under temperature changes, with a thermal expansion coefficient of 23.4 × 10^-6/K, compared to 6005's slightly higher rate of 23.8 × 10^-6/K.
What are the post-processing finishing options unique to each alloy?
6065 responds exceptionally well to chemical brightening and clear anodizing, while 6005 is better suited for hard anodizing and powder coating applications due to its surface characteristics.
How do recycling considerations differ between these alloys?
6005 has better recyclability due to its more common alloying elements, while 6065's specialized composition may require more selective recycling streams and sorting processes.
What is the typical lead time difference when ordering 6065 vs 6005?
6005 typically has shorter lead times of 2-3 weeks due to its widespread availability, while 6065 may require 4-6 weeks as it's often made to order for specific applications.


