Pure aluminum has a precise melting point of 660.32°C (1220.58°F). This temperature represents the point where solid aluminum transitions to its liquid state.
Understanding Pure Aluminum's Melting Point
Base Properties
The melting temp of aluminum is lower than many common industrial metals
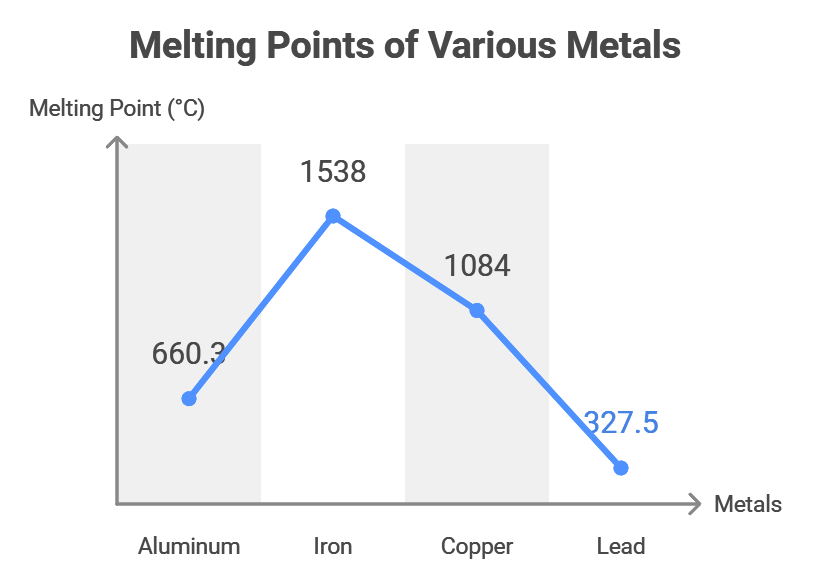
Here's a comparison:
Metal | Melting Point (°C) | Melting Point (°F) |
|---|---|---|
Aluminum | 660.32 | 1220.58 |
Iron | 1538 | 2800 |
Copper | 1084 | 1983 |
Lead | 327.5 | 621 |
Phase Transition Process
The melting process of pure aluminum occurs in distinct stages:
- Solid Phase: Below 660.32°C
- Transition Point: At 660.32°C
- Liquid Phase: Above 660.32°C
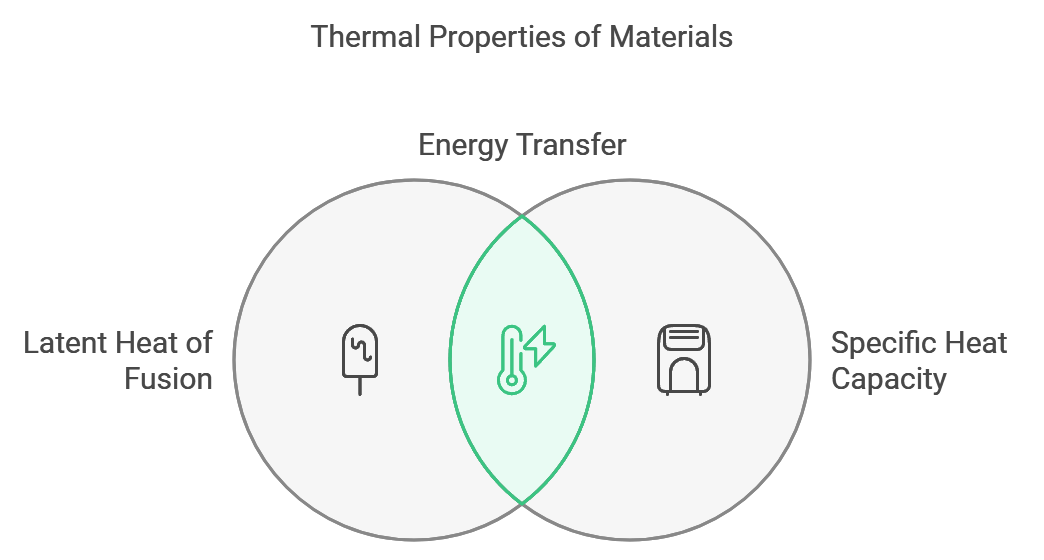
Thermal Properties
Pure aluminum exhibits specific thermal characteristics during melting:
- Latent Heat of Fusion: 397 kJ/kg
- Specific Heat Capacity: 0.897 kJ/kg·K
- Thermal Conductivity: 237 W/m·K
Industrial Grade Purity
The melting temp of aluminum varies slightly with purity levels:
Purity Level | Melting Point Range (°C) |
|---|---|
99.999% | 660.32 ±0.02 |
99.99% | 660.32 ±0.05 |
99.9% | 660.32 ±0.1 |
Melting Points of Common Aluminum Alloys
The melting temp of aluminum varies significantly across different alloy compositions. Here's a comprehensive analysis of common aluminum alloys and their melting ranges:
Commercial Alloy Series
Common aluminum alloys exhibit distinct melting ranges
Alloy | Melting Range (°C) | Melting Range (°F) |
|---|---|---|
2024 | 500 - 635 | 935 - 1180 |
3003 | 643 - 654 | 1190 - 1210 |
6061 | 582 - 652 | 1080 - 1205 |
7075 | 477 - 635 | 890 - 1175 |
A356 | 557 - 596 | 1030 - 1100 |
Binary Alloy Systems
Various binary aluminum alloys show unique melting characteristics:
Alloy Type | Melting Point (°C) | Melting Point (°F) |
|---|---|---|
Al-Cu | 548 | 1018 |
Al-Si | 577 | 1071 |
Al-Mg | 600 | 1110 |
Al-Zn | 382 | 720 |
Casting Alloys
Specialized casting alloys demonstrate different melting ranges:
Alloy | Melting Range (°C) | Melting Range (°F) |
|---|---|---|
A360 | 1030 – 1100 | 557 – 596 |
A380 | 1000 – 1100 | 538 – 593 |
A413 | 1070 – 1080 | 574 – 582 |
The change in melting point occurs due to different alloying elements and their proportions. These differences make certain alloys more suitable for specific applications, such as consumer goods manufacturing or even aerospace components.
Factors Affecting Aluminum's Melting Point
The melting temp of aluminum can vary significantly based on several key factors:
Alloy Composition
The presence of alloying elements significantly impacts the melting temperature:
- Pure aluminum melts at 660.32°C (1220.58°F)
- Different alloy compositions create varying melting ranges rather than a single point
- The addition of elements like copper can lower the melting point
Purity Levels
Material purity plays a crucial role in determining melting characteristics:
- Impurities can cause melting point depression
- A variation of more than 41 degrees Fahrenheit indicates the presence of impurities
- Higher purity levels result in more precise melting points
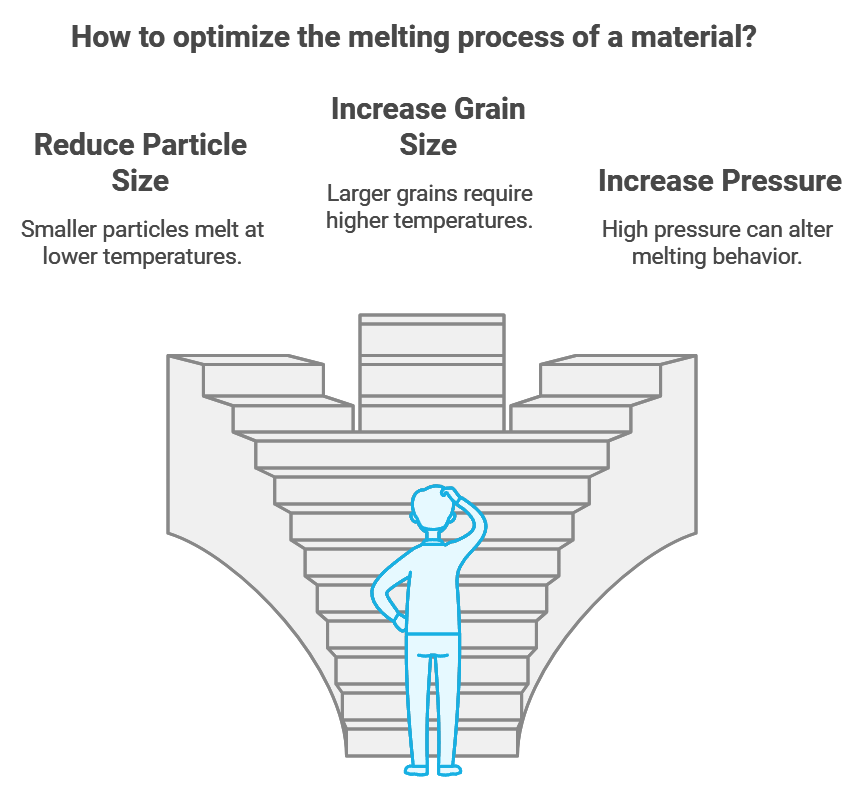
Physical Characteristics
Several physical factors influence the melting process:
Factor | Effect on Melting Point |
|---|---|
Particle Size | Smaller particles melt at lower temperatures |
Grain Size | Larger grains require higher temperatures |
Pressure | High pressure can alter melting behavior |
Manufacturing Process Effects
The material's processing history affects its melting behavior:
- Heat treatment processes can modify the microstructure
- Stress and strain within the crystal lattice can alter melting points
- Different manufacturing processes create varying molecular arrangements
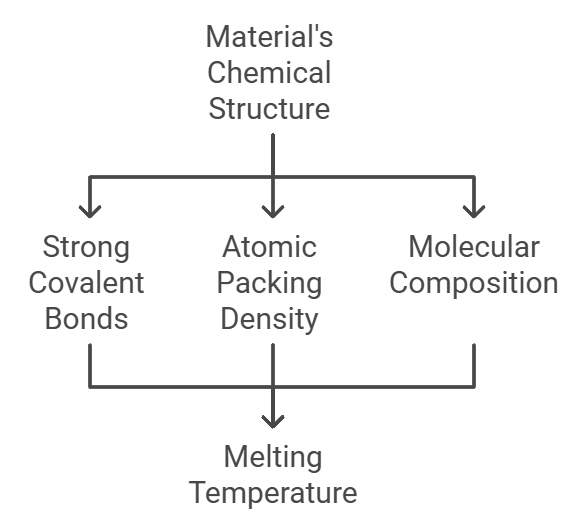
Chemical Properties
The material's chemical structure influences its melting characteristics:
- Strong covalent bonds require more energy to break
- Atomic packing density affects melting temperature
- Molecular composition impacts overall thermal behavior
Industrial Applications and Processing
The melting temp of aluminum plays a crucial role in various industrial applications and processing methods. Here's a detailed analysis:
Die Casting
- Operating temperatures: 1300-1450°F for optimal processing
- Used for high-volume production
- Creates precisely formed parts with minimal machining needs
Permanent Mold Casting
The process involves:
- Preheating the mold
- Pouring molten aluminum
- Controlled cooling for optimal structure
Sand Casting
This versatile method is ideal for:
- Small production runs
- Complex designs
- Large castings requiring intricate details
Key Industrial Sectors
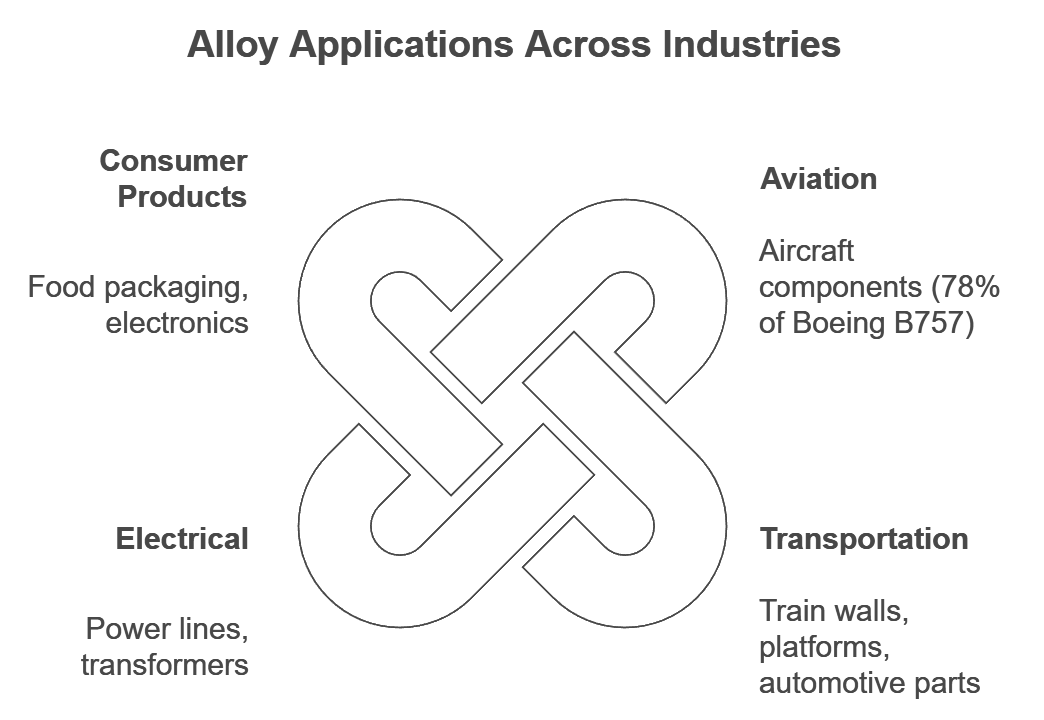
The main applications include:
Industry | Application | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
Aviation | Aircraft components (78% of Boeing B757) | Lightweight, high strength |
Transportation | Train walls, platforms, automotive parts | Fuel efficiency, durability |
Electrical | Power lines, transformers | Superior conductivity |
Consumer Products | Food packaging, electronics | Non-toxic, corrosion resistant |
Processing Considerations
Several factors affect industrial processing:
- Energy-efficient furnaces help control melting conditions
- Open well furnace designs facilitate scrap addition
- Proper temperature control prevents premature solidification
Quality Control Measures
Processing includes several verification steps:
- Flux processing
- Inert gas treatment
- Filtration
- Settling procedures
Safety and Handling Considerations
When working with aluminum at its melting temp and during general handling, several crucial safety measures must be implemented:
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Essential safety gear includes:
- Fire-retardant special fabric clothing
- Safety glasses and face shields
- Leather gloves with long cuffs
- Safety shoes
- Helmets with mesh protection for heat
Storage Requirements
Proper storage practices include:
- Maintaining clean, dry indoor storage areas
- Keeping aluminum away from other metals
- Storing vertically for proper air circulation
- Using proper packaging during transport
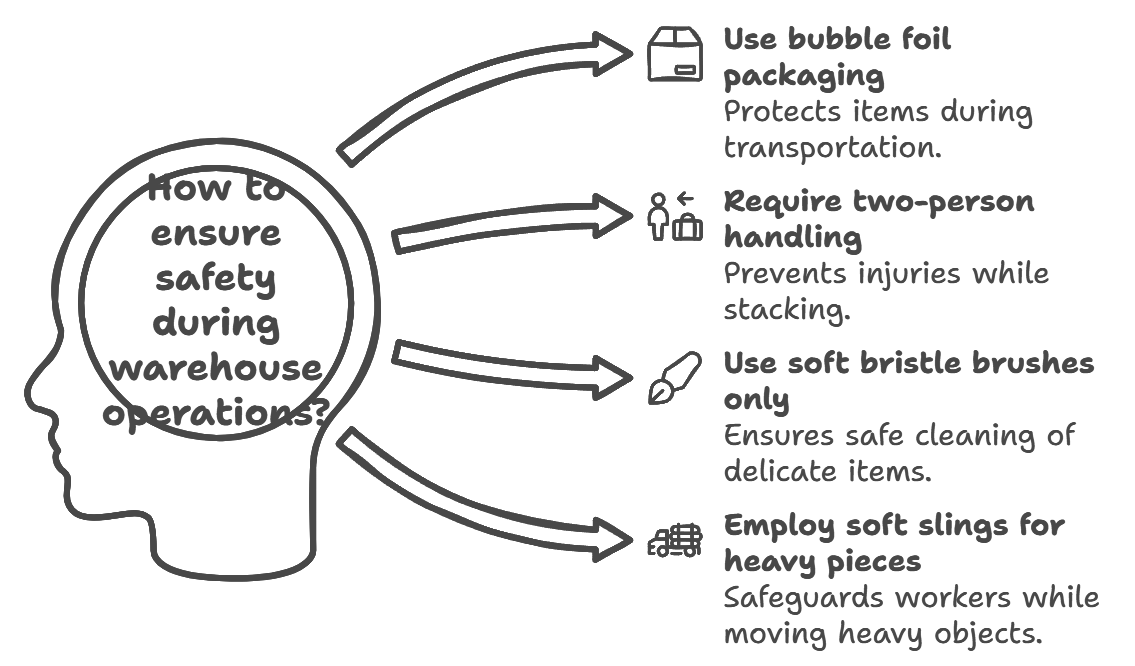
Handling Protocols
Activity | Safety Measure |
|---|---|
Transportation | Use bubble foil packaging |
Stacking | Require two-person handling |
Cleaning | Use soft bristle brushes only |
Moving | Employ soft slings for heavy pieces |
Workplace Safety Measures
Key considerations include:
- Maintaining proper ventilation systems
- Installing dust collection systems
- Keeping work areas free from moisture
- Implementing strict no-smoking policies
Hazard Prevention
Critical safety protocols:
- Monitor dust levels (limit: 15 mg/m3 over 8-hour workday)
- Prevent static electricity buildup
- Keep materials away from heat sources
- Avoid contact with water when molten
Emergency Procedures
Important safety measures:
- Maintain proper firefighting equipment
- Install emergency shower stations
- Post clear evacuation routes
- Keep first aid supplies readily available
Common Applications Based on Melting Properties
The melting temp of aluminum creates unique opportunities across various industries and applications. Here's a detailed analysis of how its melting properties are utilized:
Manufacturing Processes
Different manufacturing methods leverage aluminum's melting characteristics:
Process | Temperature Range (°C) | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
Die Casting | 660-720 | Automotive parts, electronics housings |
Sand Casting | 650-750 | Large machinery components |
Investment Casting | 660-700 | Aerospace components |
Industrial Applications
The melting properties of aluminum make it ideal for several industrial uses:
Transportation Industry
- Aircraft components require precise melting control for optimal strength
- Automotive parts benefit from aluminum's lower melting point for efficient manufacturing
- Train components utilize aluminum's heat dissipation properties
Consumer Products
- Food packaging benefits from aluminum's low toxicity and melting characteristics
- Electronic devices use aluminum for heat management
- Household appliances incorporate aluminum components for durability
Energy Sector Applications
Aluminum's melting properties play a crucial role in:
- Power transmission equipment manufacturing
- Solar panel frame construction
- Wind turbine component production
Construction Applications
The controlled melting of aluminum enables:
- Creation of structural components
- Manufacturing of window frames and doors
- Production of architectural cladding
Practical Tips for Working with Aluminum

Based on industry best practices, here are essential tips for working with aluminum safely and effectively:
Material Handling
- Use bubble foil packaging during transportation to prevent surface damage
- Store materials indoors in clean, dry conditions
- Keep aluminum in vertical position for proper air circulation
- Employ two people when handling large sheets to prevent draggin
- Use soft slings for heavy components
Surface Protection
- Inspect protective coatings upon receipt for any damage
- Check for signs of wetness to prevent water staining
- Cover surfaces with light oil for extended storage
- Remove wet products immediately before they dry
- Clean with soft bristle brushes to avoid surface damage
Equipment and Tools
- Use proper cutting tools and techniques
- Employ appropriate cutting fluids for cooling
- Ensure all electrical equipment is properly grounded
- Avoid plastic tools - use conductive materials instead
- Maintain and regularly inspect all equipment
FAQs about Melting Temp of Aluminum
What is the exact melting point of pure aluminum?
Pure aluminum melts at 660.32°C (1220.58°F), making it one of the more easily meltable industrial metals.
How do I know if aluminum contains impurities based on its melting point?
A wide melting range indicates higher impurity content, while pure aluminum has a precise melting point. The purer the material, the narrower the melting point range.
Which aluminum alloy has the lowest melting point?
Among common aluminum alloys, 7075 has the lowest melting range, starting at 475°C (890°F).
Why does aluminum melt at a lower temperature than other industrial metals?
Aluminum's relatively low melting point compared to metals like steel (1510°C) and copper (1084°C) is due to its atomic structure and bond strength.
How does the melting temperature affect aluminum's industrial applications?
The lower melting temperature makes aluminum ideal for casting, molding, and recycling processes, while still maintaining structural integrity for various applications like automotive parts and construction materials.


