Have you ever wondered why cant MLV or ELV work with any LED? While LED lighting has gained popularity due to its energy efficiency and versatility, many users face compatibility issues when pairing LEDs with traditional dimming systems like Magnetic Low Voltage (MLV) or Electronic Low Voltage (ELV).
This article explains the technical reasons for these problems and looks at ways to make LED dimming work better. We'll cover what you need to know to avoid common issues and get the most out of your LED lighting setup.

What is a MLV dimmer
A Magnetic Low Voltage (MLV) dimmer is a type of dimming control designed to work with magnetic transformers used in low-voltage lighting systems. MLV dimmers operate using leading-edge phase control technology, which means they cut off the beginning portion of each AC waveform to reduce power to the load. These dimmers are specifically engineered to handle the inductive characteristics of magnetic transformers.
MLV dimmers typically offer the following features:
What is a ELV dimmer
An Electronic Low Voltage (ELV) dimmer, also known as a trailing-edge dimmer or reverse phase control dimmer, is designed to work with electronic transformers and LED drivers. ELV dimmers operate by cutting off the trailing edge of each AC waveform, which is the opposite of how MLV dimmers function.
Key characteristics of ELV dimmers include:
Why Cant MLV or ELV Work with Any LED
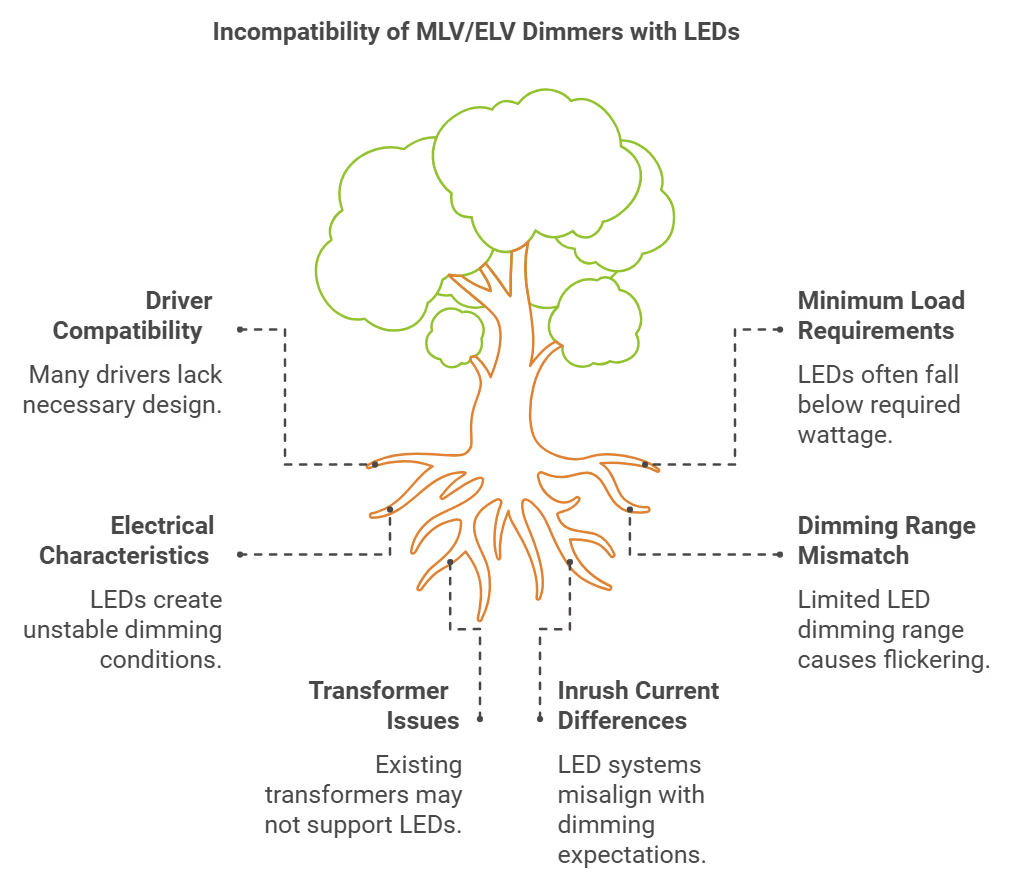
LED Driver Compatibility
MLV and ELV dimmers are designed to work with specific types of loads. LEDs require drivers to convert AC to DC power and regulate current. These drivers must be specifically designed to be compatible with the dimming method used by MLV (forward phase) or ELV (reverse phase) dimmers. Many LED drivers are not designed with this compatibility in mind, leading to issues when paired with MLV or ELV systems.
Minimum Load Requirements
MLV and ELV dimmers typically have minimum load requirements to maintain stable operation. LEDs draw significantly less power compared to the incandescent or halogen bulbs that MLV and ELV systems were originally designed for. This often results in LED loads falling below the minimum required wattage for proper dimmer function. For example, some MLV drivers require a minimum load of 20% for full-range dimming.
Electrical Characteristics
The electrical characteristics of LEDs differ from traditional lighting sources. LEDs present a more capacitive load, which can cause issues with MLV and ELV dimming systems. This can lead to unstable operation, flickering, or even complete lack of functionality. The non-resistive nature of LEDs may not properly meet the needs of the oscillator in ELV transformers, further complicating compatibility.
Dimming Range Mismatch
Even dimmable LEDs often have a limited dimming range compared to incandescent bulbs. While MLV and ELV dimmers are designed to dim incandescent lights to near 0%, many LEDs can only dim to about 10-20% of their full brightness. This mismatch in dimming ranges can cause flickering or sudden drop-outs at low dimming levels.
Transformer and Driver Issues
In retrofit situations, existing MLV or ELV transformers designed for halogen lamps may be incompatible with LED replacements. These transformers may have different minimum load requirements or may not function properly with the electrical characteristics of LEDs. To achieve proper dimming, either the transformer needs to be replaced with an LED-compatible driver, or a carefully selected compatible LED must be used.
Inrush Current and Power Factor
LEDs and their drivers can have different inrush current characteristics compared to traditional lighting sources. While MLV drivers typically have lower inrush currents, which can be advantageous, the overall power factor and current draw patterns of LED systems may not align well with MLV or ELV dimming expectations.
In conclusion, the incompatibility between MLV/ELV systems and many LEDs stems from fundamental differences in electrical characteristics, load requirements, and dimming behaviors. While some LED products are designed to work with MLV or ELV systems, universal compatibility remains a challenge due to these inherent differences.
Common Problems When Mixing Incompatible Systems
Flickering or flashing
Flickering or flashing is a common issue when MLV or ELV dimmers are used with incompatible LED systems. This can occur due to several factors:
- The dimmer switch setting may be too low, causing insufficient current to pass through the LED bulb.
- There may be a mismatch between the dimmer's minimum dim level and the LED's capabilities. Many LEDs are only designed to dim to a certain level (e.g., 5%, 10%, or 20% brightness).
- Incompatibility between the dimmer and the LED driver can cause electromagnetic interference (EMI), leading to flickering.
Limited dimming range
When MLV or ELV dimmers are used with incompatible LEDs, the dimming range is often restricted:
- LEDs may not dim smoothly throughout the entire range of the dimmer.
- The dimming may stop at a higher minimum level than expected, typically around 10-20% of full brightness.
- In some cases, the lights may suddenly turn off when dimmed below a certain point.
Premature failure of LEDs or dimming components
Incompatibility between MLV/ELV systems and LEDs can lead to premature failure of components:
- Voltage spikes from incompatible transformers can exceed the maximum voltage rating of LED driver components or the LEDs themselves.
- Constant electrical stress from improper dimming can shorten the lifespan of LED bulbs and drivers.
- Dimmer components may fail prematurely due to unexpected electrical loads from incompatible LED systems.
Audible buzzing or humming
Buzzing or humming sounds are often reported when using MLV or ELV dimmers with incompatible LEDs:
- This is typically caused by electromagnetic interference between the dimmer and the LED driver.
- The internal electronics of the LED driver may vibrate, producing an audible hum.
- Low-quality dimmer switches or incompatible combinations can exacerbate this issue.
Solutions and Best Practices
Replace MLV/ELV Dimmers with LED-Compatible Dimmers
LED-compatible dimmers are designed to work with the specific electrical characteristics of LED lights. These dimmers use pulse width modulation (PWM) to control the brightness of LED lights. PWM rapidly switches the LED on and off, with the ratio of on-time to off-time determining the perceived brightness.
LED-compatible dimmers offer several benefits:
- Smoother dimming without flickering
- Wider dimming range, often down to 1% of full brightness
- Reduced electromagnetic interference
- Better energy efficiency
LED-Specific Electrical Characteristics
LED-compatible dimmers are engineered to handle the unique electrical properties of LEDs:
- Low wattage loads
- Non-linear current-voltage relationships
- Capacitive rather than resistive loads
When MLV/ELV Must Be Used
When MLV or ELV systems cannot be replaced, you need to be careful to select compatible LEDs.
- Choose LEDs specifically rated for MLV or ELV dimming
- Look for LEDs with a wide dimming range (e.g., 100-10% or better)
- Consider LEDs with built-in dimming circuitry to improve compatibility
Limitations may still exist:
- Dimming range may be restricted (e.g., 100-20%)
- Some flickering or inconsistent performance may occur at low dimming levels
Alternative Dimming Technologies
0-10V dimming is a common alternative for LED applications:
- Uses a separate control wire to adjust brightness
- Compatible with a wide range of LED fixtures and drivers
- Offers more stable and consistent dimming performance
Considerations:
- Requires additional wiring (typically two low-voltage control wires)
- May need a compatible 0-10V LED driver for each fixture
Digital Dimming Protocols
Digital protocols like DALI (Digital Addressable Lighting Interface) and DMX offer advanced control options:
- DALI allows individual addressing of fixtures and two-way communication
- DMX provides high-speed control, often used in theatrical and architectural lighting
Benefits:
- Precise control over individual fixtures or groups
- Ability to create complex lighting scenes and effects
- Scalable for large installations
Considerations:
- Requires specialized controllers and compatible LED drivers
- More complex to set up and program than traditional dimming systems
Future of LED Dimming
Ongoing Improvements in Compatibility
As LED technology continues to advance, manufacturers are working to improve compatibility between LED lights and various dimming systems. Some key areas of focus include:
- Improved LED Drivers: LED driver manufacturers are developing more sophisticated circuitry that can better interpret and respond to different dimming signals, such as those from MLV and ELV systems. This can lead to smoother dimming performance and reduced compatibility issues.
- Adaptive Dimming Technology: Some LED drivers now incorporate adaptive dimming technology, which allows them to automatically adjust to the characteristics of the connected dimmer. This can help ensure optimal performance even with older or less compatible dimming systems.
- Industry Standards and Certifications: Organizations like NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association) are working to establish standards and certification programs for LED dimming compatibility. The NEMA LED Dimming Compatibility Program, for example, helps consumers identify LED bulbs and dimmers that are designed to work together.
Emerging Universal Dimming Technologies
In addition to improving compatibility with existing dimming systems, the lighting industry is also developing new, universal dimming technologies specifically designed for LED lighting. Some promising developments include:
- Digital Dimming Protocols: Digital protocols like DALI (Digital Addressable Lighting Interface) and DMX512 provide a standardized way to control LED lighting systems. These protocols allow for more precise and flexible control, and they are not tied to specific dimming hardware.
- Wireless Dimming Solutions: Wireless technologies like Zigbee and Bluetooth are being integrated into LED lighting systems, enabling dimming control via smartphones, tablets, and other devices. These solutions offer greater convenience and flexibility, as well as the potential for integration with other smart home systems.
- Power over Ethernet (PoE) Lighting: PoE technology allows both power and data to be delivered to LED lights over standard Ethernet cables. This enables centralized control and dimming of LED lighting systems, as well as integration with building automation systems.
As these technologies continue to evolve and gain adoption, they may help to simplify LED dimming and reduce the compatibility challenges associated with traditional dimming systems like MLV and ELV. However, it will likely take time for these new technologies to fully replace existing dimming infrastructure in many applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I use an MLV or ELV dimmer with non-dimmable LEDs?
No, you should never use a dimmer with non-dimmable LEDs. Non-dimmable LEDs are not designed to handle the varying voltage from a dimmer and can be damaged or cause the dimmer to malfunction. Always make sure to use dimmable LEDs that are compatible with your specific dimmer type (MLV, ELV, etc.).
Is it okay to mix different types of LED bulbs on the same dimmer?
Mixing different types or brands of LED bulbs on the same dimmer is not recommended, even if they are all dimmable. Different LEDs can have varying electrical characteristics that may cause compatibility issues when used together. For the best dimming performance, use identical LED bulbs from the same manufacturer on a single dimmer.
Why do my LED bulbs turn off completely before reaching the lowest dimming level?
This issue, known as "drop out," occurs when the minimum voltage required to keep the LEDs lit is higher than the lowest voltage the dimmer provides. It is more common with MLV and ELV dimmers, which were originally designed for higher-wattage incandescent loads. To minimize drop out, choose LED bulbs and dimmers that are specifically designed for compatibility with each other.
Can I use an ELV dimmer with an MLV transformer or vice versa?
No, ELV dimmers should never be used with MLV transformers, and MLV dimmers should never be used with ELV transformers. Doing so can cause damage to the dimmer, transformer, or LED fixture. Always match the dimmer type to the transformer type for safe and proper operation.
How many LED bulbs can I safely use on one dimmer?
The maximum number of LED bulbs on a dimmer depends on the wattage of the bulbs and the dimmer's rated capacity. As a general rule, add up the wattages of all the LED bulbs and ensure the total is below the dimmer's maximum load rating. However, for optimal performance, it's best to stay well below the maximum and perform field testing with your specific combination of dimmer, transformer, and bulbs.
What should I do if I'm still experiencing flickering or other issues after installing a compatible dimmer and LEDs?
If you've carefully selected compatible components and are still having issues, consider the following:
- Verify all bulbs are the same type and from the same manufacturer
- Check for loose connections or wiring issues
- Ensure the dimmer's low-end trim is adjusted properly for the specific bulbs
- Test with a smaller number of bulbs on the circuit
- Consult with the dimmer and/or bulb manufacturer for additional troubleshooting steps
In some cases, an electrician or lighting professional may be needed to diagnose and resolve complex dimming issues.


