Are you curious about the zinc composition of brass H62? This alloy contains 36-38% zinc, enhancing its strength and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for applications that require both durability and performance. In this article, you will learn in depth about the brass h62 structure.
What is H62 brass?
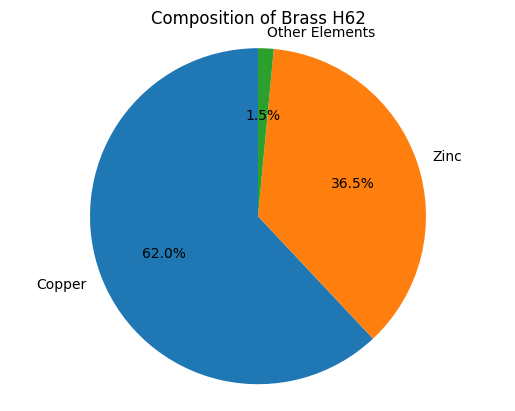
H62 brass is an alloy composed of approximately 62% copper and 38% zinc. This composition provides the material with specific properties such as enhanced plasticity and good machinability, which facilitate both hot and cold processing techniques. The alloy is commonly utilized in the manufacture of mechanical components, water supply and drainage fittings, medals, and decorative items due to its balance of strength and corrosion resistance. The formability of H62 brass also supports its use in applications requiring detailed shaping and durability. These characteristics make H62 brass a preferred material in various engineering and decorative contexts.
What is the Zinc Composition of Brass H62?
Table 1: The Brass h62 Structure
Element | Composition (%) |
|---|---|
Copper (Cu) | 60.5 - 63.5 |
Iron (Fe) | ≤ 0.15 |
Lead (Pb) | ≤ 0.08 |
Zinc (Zn) | Balance |
Antimony (Sb) | ≤ 0.005 |
Bismuth (Bi) | ≤ 0.002 |
Phosphorus (P) | ≤ 0.01 |
The zinc composition of H62 brass typically ranges from 36% to 38%, with copper generally constituting about 60.5% to 63.5% of the alloy. Trace elements such as lead, iron, and beryllium may also be present in minimal quantities.
Zinc plays a crucial role in defining the mechanical properties of H62 brass. It contributes to the hardness and strength of the alloy, while also enhancing its corrosion resistance. This makes H62 brass particularly suitable for applications requiring good durability and resistance to environmental degradation. The presence of zinc also affects the alloy's thermal and electrical conductivity, albeit to a lesser extent compared to its structural and corrosive properties.
In practical terms, the specific zinc content within the noted range influences how the brass behaves during processing and in its final application. Higher zinc content generally leads to increased strength and hardness, making the alloy suitable for components that must endure more significant mechanical stress or wear.


Mechanical and Physical Properties
Table 2: The Properties of H62 Brass
Property | Value |
|---|---|
Tensile Strength (MPa) | 370 - 420 |
Yield Strength (MPa) | 260 - 300 |
Elongation (%) | 10 - 15 |
Hardness (Vickers) | 100 - 140 VHN |
Hardness (Rockwell B) | 60 - 80 HRB |
Density (g/cm³) | 8.4 - 8.5 |
Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | 120 - 150 |
Corrosion Resistance | Good |
Wear Resistance | Moderate to Good |
Tensile Strength and Yield Strength
H62 brass, as a commonly used alloy, displays a tensile strength typically in the range of 370 to 420 MPa. This metric indicates the maximum stress that H62 brass can withstand while being stretched or pulled before breaking. The yield strength, generally between 260 to 300 MPa, marks the stress at which a permanent deformation of 0.2% of the original dimension occurs. These properties make H62 brass suitable for applications requiring moderate strength and good formability.
Elongation and Hardness (Vickers and Rockwell)
The elongation of H62 brass, which typically lies between 10% and 15%, reflects its ability to undergo plastic deformation prior to fracturing. This measure is crucial for processes involving bending and forming. In terms of hardness, the alloy is assessed via the Vickers and Rockwell (B scale) hardness tests, with typical values ranging from 100 to 140 VHN and 60 to 80 HRB, respectively. This hardness level contributes to the alloy's resistance to surface wear and deformation under load.
Density and Thermal Conductivity
H62 brass has a density of approximately 8.4 to 8.5 g/cm³, influencing its weight and structural applications where mass is a consideration. Its thermal conductivity, important in applications such as heat exchangers and radiator components, typically spans from 120 to 150 W/m·K. This high thermal conductivity facilitates the efficient transfer of heat, beneficial in cooling systems and other thermal applications.
Corrosion Resistance and Wear Resistance
The corrosion resistance of H62 brass is characterized by its ability to withstand degradation from environmental exposure, including from moisture and atmospheric conditions. This property is particularly enhanced by its zinc content, which contributes to the formation of a protective oxide layer. Wear resistance in H62 brass is considered moderate to good, making it suitable for components that experience regular physical contact and friction, ensuring longevity and reliability in such applications.


Manufacturing and Processing
Table 3: The Manufacturing of H62 Brass
Process Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
Workability | Excellent in both hot and cold conditions |
Manufacturing Processes | Casting, extrusion, drawing, forging |
Typical Defects | Porosity, anisotropy |
Defect Remedies | Process parameter optimization, controlled cooling |
Hot and Cold Workability
H62 brass exhibits excellent plasticity in both hot and cold states, which significantly enhances its workability. This dual-phase alloy, comprising alpha and beta phases, displays distinct flow characteristics under different temperatures and deformation rates, which are crucial for understanding its formability during manufacturing processes. The alpha phase, for instance, flows more readily at temperatures below 400°C, whereas the beta phase becomes more malleable and prone to deformation at higher temperatures, especially beyond its transition temperature of 500°C.
Common Manufacturing Processes: Casting, Extrusion, Drawing, Forging
H62 brass is commonly shaped through various manufacturing processes, including casting, extrusion, drawing, and forging. The alloy is well-suited for continuous casting and up-drawing continuous casting, where its flow properties and phase coordination play a vital role in achieving desired structural characteristics. This adaptability makes it a preferred material for producing complex cross-sectional wires and profiles, particularly through processes that benefit from its excellent thermal deformation behavior and heat treatment responsiveness.
Typical Defects in Manufacturing and Their Remedies
During the manufacturing of H62 brass, several typical defects can occur, such as porosity in casting and anisotropy in mechanical properties due to uneven cooling and phase transformation. To mitigate these defects, precise control of process parameters like temperature and deformation rate is critical. Additionally, employing optimized cooling and heat treatment schedules can help refine grain structures and enhance overall material properties. The use of numerical simulations and advanced optimization algorithms, such as the Kriging model and particle swarm optimization, has proven effective in identifying optimal process parameters to minimize defects and improve the quality of the final product.
Applications of H62 Brass
Table 4: The Applications of H62 Brass
Application Category | Examples of Applications |
|---|---|
Electrical Components | Connectors, terminals, circuit board components |
Mechanical Parts | Springs, screens, radiator parts |
Building Materials |
Electrical Components and Connectors
H62 brass is extensively utilized in the electronics sector due to its excellent electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance. This alloy is a popular choice for manufacturing connectors, circuit board components, and other electronic parts that require precise conductivity and durability.
Mechanical Parts
The mechanical strength, good corrosion resistance, and excellent malleability of H62 brass make it ideal for various mechanical applications. It is commonly used in the production of springs, screens, and radiator components. These applications benefit from the alloy’s ability to withstand mechanical stress and environmental exposure, ensuring longevity and reliability in performance.
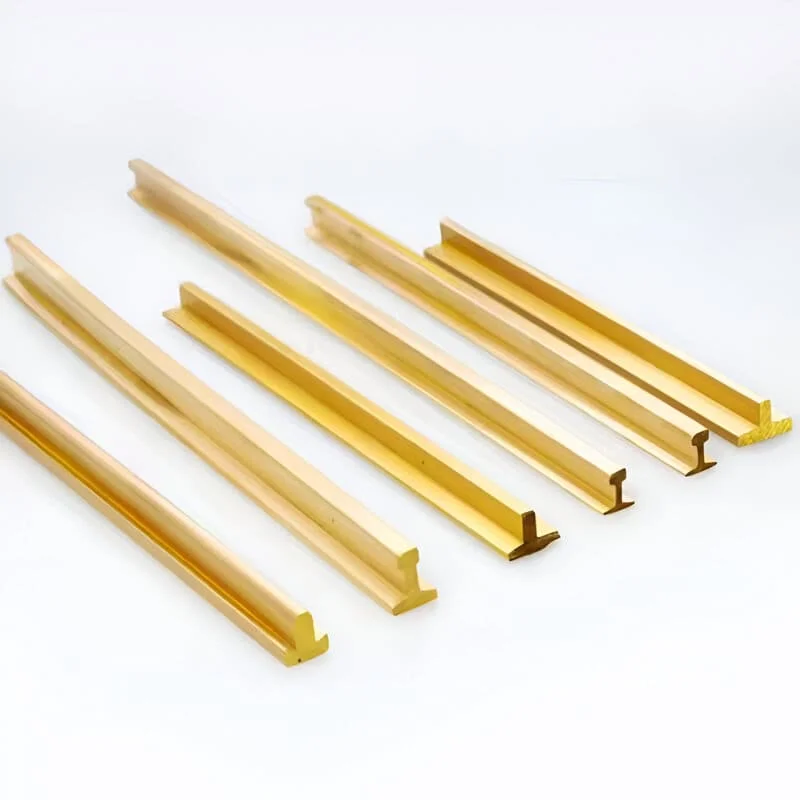
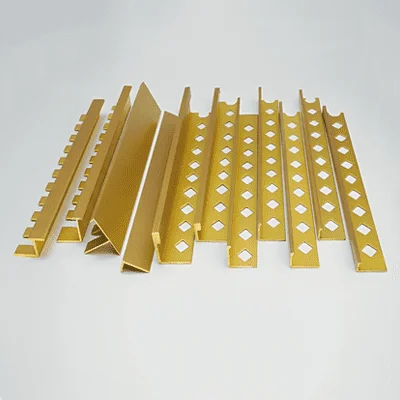




Building Material Decorative Items
In the building materials sector, H62 brass is favored for its aesthetic qualities and durability, making it suitable for decorative applications such as brass tile trims, strips, bars, transition strips, and stair nosing. These products are often used in both interior and exterior architectural designs to add a touch of elegance and resistance to wear and corrosion. The alloy’s versatility also extends to general construction materials, where it contributes to the structural integrity and visual appeal of buildings.
Corrosion Behavior
Overview of Dezincification and Its Impact
Dezincification is a form of corrosion that specifically affects brass alloys like H62, involving the selective leaching of zinc from the alloy. This process leaves behind a porous structure primarily composed of copper, which is mechanically weaker and more susceptible to further corrosion. The impact of dezincification is particularly severe in environments with high chloride ion concentrations, such as marine atmospheres, where it can significantly degrade the material's structural integrity and lead to premature failure of brass components.
Strategies to Mitigate Corrosion in High-Zinc Alloys
To mitigate the effects of dezincification in H62 brass and other high-zinc alloys, several strategies are commonly employed:
- Alloy Modification: Adjusting the composition of the brass alloy by reducing the zinc content or adding small amounts of other elements like arsenic, antimony, or phosphorus can enhance corrosion resistance. These elements act to inhibit the leaching process by stabilizing the alloy structure against zinc loss.
- Protective Coatings: Applying surface treatments such as chromate, phosphate, or polymeric coatings can provide a protective barrier that prevents the corrosive media from directly contacting the brass surface. These coatings are particularly effective in environments with high corrosion potential, like saltwater exposure.
- Environmental Control: Reducing exposure to aggressive environments by using design considerations to avoid stagnant water conditions and ensuring good drainage can also decrease the risk of dezincification. Regular maintenance and inspection routines help in early detection and remediation of potential corrosion sites before significant damage occurs.
By integrating these strategies, the lifespan and reliability of H62 brass components in corrosive environments can be substantially improved, ensuring their functionality and structural integrity over time.

What is the difference between H62 and H59 brass?
Table 5: Comparison of H62 and H59 Brass
Property | H62 Brass | H59 Brass |
|---|---|---|
Copper Content | 60.5-63.5% | 59-62% |
Zinc Content | Balance | Balance |
Tensile Strength | 290-360 MPa | 315-350 MPa |
Yield Strength | Moderate | Higher |
Hardness | Moderate | Higher |
Ductility | Higher, better formability | Good, but slightly less |
Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, slightly better in harsh environments | Excellent, but marginally lower |
Thermal Conductivity | High | High |
Electrical Conductivity | High | High |
Cost | Slightly higher | Slightly lower |
Common Applications | Electrical components, ammunition casings, decorative arts | Machine parts, welding parts, hot stamping, electrical appliances, electronics, lighting, hardware |
Formability | Better machinability and formability | Good, but slightly less |
Hot Working Temperature | 650-850°C | 730-820°C |
Annealing Temperature | 600-670°C | 600-670°C |
Standards | GB H62, C28000, CuZn38 | GB H59, C37700 |
How to Choose the Right H62 Brass?
Choosing the right material for your project is crucial for ensuring optimal performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Here’s a guide to help you determine when H62 brass is the best choice for your needs:
When to Choose H62 Brass
- Corrosive Environments:
- If your application will be exposed to marine or coastal environments, H62 brass's excellent corrosion resistance makes it a suitable choice.
- High Formability Needs:
- Choose H62 brass if your project requires extensive forming, bending, or drawing. Its high ductility allows for intricate shapes and designs.
- Aesthetic Requirements:
- For applications where appearance is important, such as decorative arts or architectural elements, H62 brass’s attractive golden color and ability to take on various finishes make it ideal.
- Electrical Applications:
- H62 brass is a good choice for electrical components due to its excellent electrical conductivity.
- Moderate Mechanical Strength:
- If your application requires moderate mechanical strength without sacrificing formability, H62 brass provides a good balance.
- Regulatory Compliance:
- Opt for H62 brass if you need to meet stringent regulatory requirements regarding lead content, as it has lower lead levels compared to other brass alloys.
- Cost Considerations:
- While H62 brass is slightly more expensive than some other brass alloys, its benefits in terms of corrosion resistance and formability can justify the cost for specific applications.
FAQs about the Zinc Composition of Brass H62
Q: What is the density of Brass H62?
A: The density of Brass H62 is approximately 8.43 g/cm³.
Q: How does the zinc content affect the properties of Brass H62?
A: The zinc content in Brass H62 enhances its strength and flexibility. It also improves corrosion resistance and machinability, making it suitable for various applications.
Q: Why is Brass H62 preferred for electrical applications?
A: Brass H62 is preferred for electrical applications due to its high electrical conductivity, which can reach more than 98% of that of pure copper.
Q: Is Brass H62 easy to machine and form?
A: Yes, Brass H62 has good plasticity in both hot and cold states, making it easy to machine and form into intricate shapes.
Q: What is the color of Brass H62?
A: Brass H62 typically has a yellowish color, which can vary depending on the exact zinc content.

